According to Statista, the estimated losses to online fraud were about 20 billion US dollars in 2021.
During the Covid-19 crisis, even more, people started shopping online, and those with less experience were more prone to eCommerce fraud.
Online merchants also reported a notable increase in online fraud, which made it much harder to run an eCommerce business.

That is not to say that cybersecurity threats were not present before the pandemic hit. No, if anything, the issue has been current since eCommerce’s inception. It is just that the prominence at which the threats are rising and affecting different online stores has grown so much that raising awareness has become a necessity.
This article aims to explain the most common eCommerce security threats and cover methods used to counter these threats. Let’s start with the threats.
eCommerce Threats
E-Skimming
One of the most recent malicious software making rounds on the Internet is e-skimming. The purpose of this threat is to infect checkout pages of online stores. If the attack is successful, the owner of e-skimming malware can get their hands on shopper personal and payment information.
Phishing
Some shoppers might receive text messages or emails from hackers pretending to be actual store owners.
This kind of fraud is quite common, especially when a hacker learns what email address or mobile number a customer used to register in a store.
A hacker tries tricking a customer into submitting credentials and exposing them for personal gain by presenting a fake copy of a website or another type of content.
Financial Frauds
Financial fraud is one of the most common eCommerce threats. Unauthorized transactions are not easy to track, especially for businesses that process hundreds or thousands of transactions daily.
Some fraudsters also acquire goods illegally and try to refund them to stores with the intent to make money in what seems like a legitimate way.
Trojans
Attackers succeed in infecting the computers of website administrators or shoppers with Trojan Horses. Some users fail to use antivirus software and other means of securing themselves, resulting in a security problem.
Spamming
Spam attacks are pretty annoying. You might wake up to see your website filled with random comments and fishy URLs. If there is a contact form, the email inbox could also be spam.
In addition to exposing a website’s security, spam attacks also cause overall performance issues by slowing it down.
DoS and DDoS
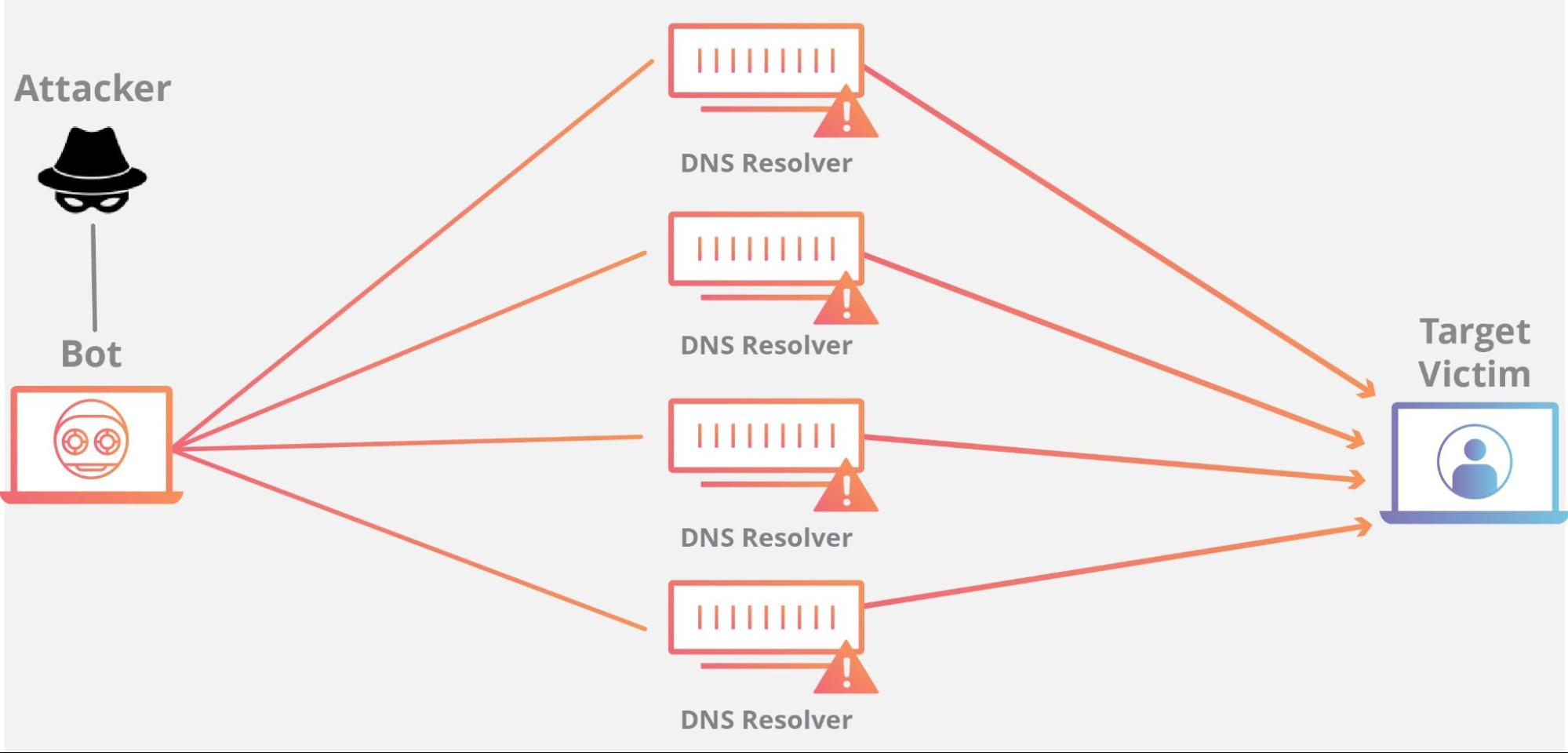
A website can take only so many requests from different IP addresses. A barrage of attacks from many untraceable IPs is known as DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service). Once the website cannot cope with the load from these attacks, it goes down.
Brute Force Attacks
Unlike DDoS attacks, brute force attacks are aimed at the website’s admin panel. The goal of the attack is to brute force a way to figure out the admin credentials and access the panel.
Software that can quickly go through different login and password combinations can crack the details. Once a hacker gets the admin credentials, they are usually free to do whatever they want with the online store.
Bots
As a rule of thumb, online website owners need to protect themselves from bots. Some hackers focus on developing bots to scrap the store’s information about prices and inventory. The competition uses the details, for example, to drive down the prices and offer better deals for shoppers.
Man in the Middle
A poorly protected online website is easy to breach, and someone might be watching a conversation between the website and its customers. What is known as the man in the middle is a popular cybersecurity threat, and it is up to the hacker what they want to do with the information after successfully hacking the website.
SQL Injections
SQL injections attack query submission forms. The goal is to gain access to a website’s database.
The attack injects a malicious code and uses it to absorb the information in the database. Once the data collection is over, the attacker deletes the code to remove any traces of its existence.
Methods to Secure Your Online Store
With potential threats out of the way, it is time to discuss methods to secure the website. As a rule of thumb, the more precautions the website has, the lower the odds of becoming a successful hacker target.
#1 – Staff and Client Education
Start with training your staff. Everyone who works on developing the online store should be aware of potential threats.
Also, keep an eye on everyone who has credentials and can access the site’s backend. Those who can access sensitive customer information, especially on live chat software and other essential aspects of the site must be monitored carefully.
It is worth noting that cybersecurity-related issues are not necessarily related to your staff. The customers themselves are also responsible. Lapses happen due to carelessness and ignorance. For instance, a shopper might be in danger because they have clicked on a shady URL and infected their computer or smartphone.
A regular newsletter covering the latest in cybersecurity with an emphasis on how customers can improve their online privacy and security should not be too much of an effort for a business to create and send out. The shoppers will also appreciate the valuable information, which is an added bonus.
#2 – The Right Ecommerce Solution Option
Shopify, PrestaShop, and WooCommerce are some of the most popular eCommerce platforms that excel in security features. It would be a waste not to pick an e-commerce solution that offers the right security tools in addition to its features.
Since the most popular e-commerce platforms compete with one another, they put a lot of effort into ensuring that the users are satisfied, including security. Regular updates and multiple security tools make things easier for users.
Instead of developing an online store from scratch and struggling with cybersecurity-related issues, you can simplify the process with the right eCommerce solution.
#3 – Data Backups
Data backups are not a direct way to prevent cybersecurity threats, but that does not mean you should undermine the importance of a backup.
As a precaution, data backups can do wonders for the website’s security. In case something happens, you will have the option to restore the website to its previous version and start again. Only this time will you know about the threat and can take the necessary measures to prevent it in the future.
Depending on the eCommerce platform of your choice, you might have no access to built-in backup tools. As such, look for a third-party solution or contact customer support and ask whether they can offer some suggestions.
Ideally, the backups should be set to occur automatically. And if you can afford it, use multiple backup tools for that extra security.
#4 – Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure
HTTP protocols are outdated and are often flagged by Internet browsers. There is no universal imperative for websites to use HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure), but missing the protocol is not a good sign.
The purpose of the secure protocol is to protect sensitive information submitted by shoppers, such as their credit card details or login credentials.
Missing HTTPS also hinders the website’s ranking. Google itself has officially confirmed that it considers HTTPS as a ranking factor.
#5 – Payment Gateway Security

Do not store customer credit card details on your website. There is no telling what will happen if the parties get exposed. It might just be enough to spell the end of your business due to how damaging data breaches can be to one’s reputation.
The easiest way to circumvent potential payment gateway security issues is to rely on third-party payment gateways. Services like Payoneer, Stripe, PayPal, and Skrill are the go-to options.
#6 – Smart Password Policy
The habit of changing passwords regularly and using complicated combinations is not something many people have.
The reluctance to bother is usually justified by the fact that they were never personally affected by a cybersecurity threat. Such an attitude is not great when you are someone who uses passwords to access a store’s admin panel.
What happens if someone figures out your password because it was easy to crack? Or what about those who use the same password for everything and get their details exposed?
Yes, using different and complicated passwords for other accounts is annoying, but you do not have to memorize them. Instead, stick to a password manager and store the details you can only access with a master password.
Also, whenever possible, use two-factor authentication. Even if someone figures out their password, they will still be stopped. Unlike the rightful owner of the account, they will not have access to an email or a smartphone that is used to receive a code as a second confirmation step.


